We can obtain the exact evaluation of the sensibility
of system (1) using the system depending on
a parameter
![]()
where ![]() ,
,
![]() and
and ![]() If A is a regular matrix, then
If A is a regular matrix, then ![]() is a differentiable function of the parameter
is a differentiable function of the parameter ![]() in some neighbourhood of the value 0. Differentiating the both sides of
equality (3) with respect to the parameter
in some neighbourhood of the value 0. Differentiating the both sides of
equality (3) with respect to the parameter ![]() ,
we get
,
we get
![]()
and
![]()
It follows from relation (4) that
![]()
Let us write the first order Taylor formula for the
function ![]()
![]()
As the result, we obtain for arbitrary vector norm and for the matrix norm
corresponding to it
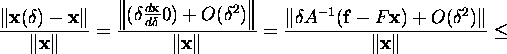
![]()
Taking into account that from relation (1)
it follows ![]() we obtain the evaluation
we obtain the evaluation
![]()
or
![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are the relative
errors of the matrix A and the vector
are the relative
errors of the matrix A and the vector ![]() ,
respectively.
,
respectively.
Proposition 8.2.1.
If ![]() is a regular matrix, then the relative
error
is a regular matrix, then the relative
error ![]() of the solution of the linear system (1) corresponding
to the relative error
of the solution of the linear system (1) corresponding
to the relative error ![]() of the matrix A and the relative
error
of the matrix A and the relative
error ![]() of the vector
of the vector ![]() is given by
is given by
![]()
Corollary 8.2.1. In
case of the Euklidean norm it holds the estimation
![]()
Proof. The relation ![]() holds. As the matrix A is regular, it follows from its singular
value decomposition
holds. As the matrix A is regular, it follows from its singular
value decomposition ![]() that
that ![]() where
where ![]() Since
Since ![]() then
then ![]() and
and
![]()
Example 8.2.1.* Let us estimate the
relative error
![]() of the solution
of the solution ![]() of the system
of the system ![]() in case of the Euclidean norm if
in case of the Euclidean norm if
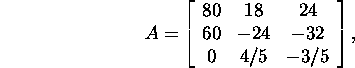
![]() and
and ![]()
Let us find the singular decomposition
of the matrix A
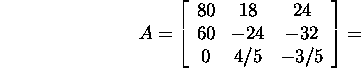
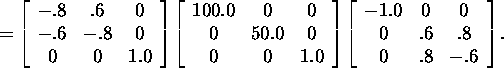
In virtue of corollary 8.2.1, we can state
![]()
Problem 8.2.1.* Estimate the relative
error ![]() of the solution
of the solution ![]() of the system
of the system ![]() in case of the Euclidean norm if
in case of the Euclidean norm if
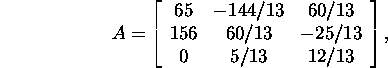
![]() and
and ![]()
Remark 8.2.1. Kahan (1966) proved that
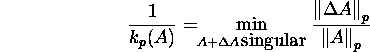
and Rice (1966) proved that
![]()