Definition 1.5.1. A vector
space ![]() (over the number field
(over the number field ![]() )
is called a normed space, if to each vector
)
is called a normed space, if to each vector ![]() there corresponds a certain non-negative real number
there corresponds a certain non-negative real number ![]() called the norm of the vector, such that the following conditions
are satisfied:
called the norm of the vector, such that the following conditions
are satisfied:
1. ![]() identity axiom);
identity axiom);
2. ![]() (
(![]() ogencity
axiom);
ogencity
axiom);
3. ![]() (triangle inequality).
(triangle inequality).
Definition 1.5.2. The distance
![]() between two vectors in the normed space
between two vectors in the normed space ![]() is defined by the formula
is defined by the formula ![]()
Proposition 1.5.1 (Hölder
inequality). If ![]()
![]()
then
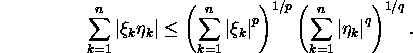
Proof. See E.Oja, P.Oja (1991, pp. 11-12).
Proposition 1.5.2
(Minkowski inequality). If ![]()
![]()
then
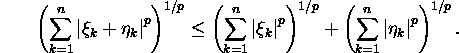
Proof. See E.Oja, P.Oja (1991, pp. 10-11).
Example 1.5.1. One defines
in ![]() the p-norm
the p-norm ![]() of the vector
of the vector ![]() by the formulas
by the formulas
![]()
![]()
Let us verify that the p-norm ![]() satisfies the conditions 1-3 in definition 1.5.1:
satisfies the conditions 1-3 in definition 1.5.1:
![]() ;
;
![]()
![]()
using the Minkowski inequality,
we get
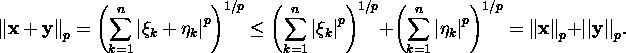
Verify conditions 1-3 in case of the norm ![]() !
!
The most often used p-norms are:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Problem 1.5.1.* Let be given
the vectors ![]() ja
ja ![]() Find
Find
![]()
![]()
Proposition 1.5.3. All the p-norms of the
space ![]() are equivalent, i.e., if
are equivalent, i.e., if ![]() and
and ![]() are the p-norms of the space
are the p-norms of the space ![]() ,
then there exist positive constants c1 and
,
then there exist positive constants c1 and ![]() such that
such that
![]()
At the same time
![]()
![]()
![]()
Let us prove the last three assertions:
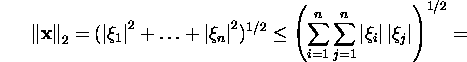
![]()
Using the Hölderi inequality, we get
in case p=q=2 that
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Proposition 1.5.4. A
space with scalar product ![]() is a normed space with the norm
is a normed space with the norm
![]()
Proof. Let us verify the validity of conditions
1-3:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is the notation for the real part of the complex number
is the notation for the real part of the complex number ![]()
Proposition 1.5.5.
In the normed space with scalar
product it holds the parallelogram rule:
![]()
Proof. By the immediate check, we get
![]()
![]()
![]()
Definition 1.5.3.
It is said that the sequence ![]() of the elements of the space
of the elements of the space ![]() converges with respect to the p-norm to the element
converges with respect to the p-norm to the element ![]() if
if
![]()
In this case we shall write ![]()
Remark 1.5.1. Since all the p-norms
of the space ![]() are equivalent, this implies that the convergence of the sequence
are equivalent, this implies that the convergence of the sequence ![]() with respect to the
with respect to the ![]() -norm
will yield its convergence with respect to the
-norm
will yield its convergence with respect to the ![]() -norm.
-norm.
Problem 1.5.2. Show that if ![]() ,
then
,
then ![]()
Problem 1.5.3. Show that if ![]() ,
then
,
then
![]()
where ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
![]() .
Find such a constant cn, that
.
Find such a constant cn, that
![]()
Definition 1.5.4.
A vector ![]() is called an approximation to the vector
is called an approximation to the vector ![]() if it differs little from
if it differs little from ![]() in some sense.
in some sense.
Definition
1.5.5. In case of the fixed norm ![]() ,
the quantity
,
the quantity
![]()
is called the absolute error of the approximation ![]() to the vector
to the vector ![]() and the quantity
and the quantity
![]()
is called the relative error of the approximation (![]() ).
).
In case of the ![]() norm
the relative error can be considered as an index of the correct significant
digits. Namely, if
norm
the relative error can be considered as an index of the correct significant
digits. Namely, if ![]() then the greatest component of the vector
then the greatest component of the vector ![]() has k correct significant digits.
has k correct significant digits.
Example 1.5.2. Let ![]() and
and ![]() Find
Find ![]() and
and ![]() ,
and then the number of the correct significant digits of the greatest component
of the approximation
,
and then the number of the correct significant digits of the greatest component
of the approximation ![]() by
by ![]() .
We get
.
We get ![]() ja
ja ![]() and
and ![]() Thus the greatest component
Thus the greatest component ![]() of
of ![]() has three correct significant digits. At the same time, the component
has three correct significant digits. At the same time, the component ![]() has only one correct significant digit.
has only one correct significant digit.